Archive for the ‘Marc Tucker’ Tag
Update 3/8/16 – Friends in Ohio and Florida have confirmed that this exact bill (elimination of elected school boards) is being pushed there. Watch the “greedom-over-freedom” ed-tech lobbies, such as Jeb Bush’s Foundation for Excellence in Education, Global Silicon Valley investment group, Bill Gates, Marc Tucker’s National Center on Education and Economy, and Pearson, whose investments benefit from the streamlined elimination of voter input.
The bill in Utah has passed the Senate and is being considered in the House with a (pointless) amendment that would add to the appointed dictator-superintendent, an appointed-not-elected board. Several House members are opposing the bill right now. One rare senator who voted against the bill said in an email, “I couldn’t believe this may pass with no input – I like that the voters will determine if this goes to the ballot, but it’s a lot to explain to voters.” Yes, it is!
I’ve added contact emails for senators and representatives below.

SJR16, Senator Jim Dabakis’ bill to abolish the voice of voters in Utah education by abolishing the elected State School Board, passed the Utah Senate this week.
An article in the Salt Lake Tribune states: “Dabakis argued that the change would empower voters”.
Dabakis’ claim is a ridiculous lie. The very short bill (SJR16) has only two elements, as it slashes at the Utah Constitution: 1) to eliminate the elected board, and 2) to have no election and no representation at all. A solitary, governor-appointed superintendent would supervise all of Utah’s education system by him/herself.
This bill puts voters dead last, of course– because no vote will ever select the governor-appointed, solo-flying, unremovable superintendent.
An email from a Utah legislator who supports SJR16 argued: “Think of the current state board as a school bus with fifteen different steering wheels all driving in different directions….if one person is in charge, it’s harder for them to pass the buck.”
If he applied that reasoning to his own seat in the legislature, then there should be no legislature, but a king instead. And if the Senate gets the House to agree, and if the voters agree, then there will be an Education King of Utah.
It is up to the members of the House of Representatives to kill this awful bill that the Senate has approved. If they don’t, voters get one chance to end it. But will they? Will we all take the time to look at the history surrounding this long-planned effort?
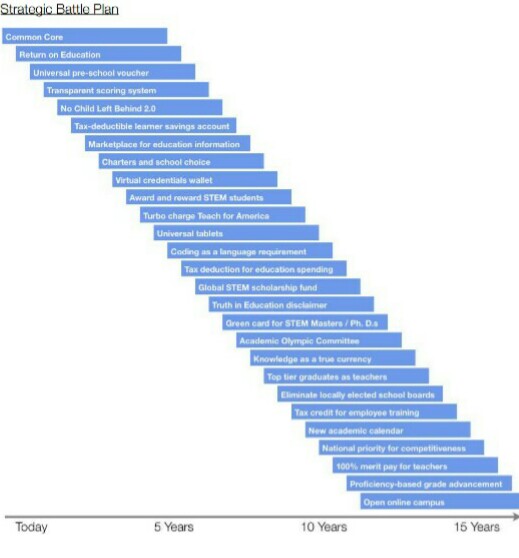
This bill may have been sponsored by the notorious Democrat Jim Dabakis, but he didn’t come up with the idea of eliminating elected school boards. Blatant enemies of local control came up with the idea years ago and their ploy is ticking along even better than they’d planned. See the GSV’s graphic below. The “battle plan” of this investment company started with Common Core, and about ten years later, it planned to eliminate school boards. Utah’s leadership is listening to and acting on these plans —because of investment. Because dollars speak more loudly than children do.
Look at two movers and shakers from outside Utah, who are shaping Utah policy in this direction. One is a socialist and the other is a corporate hog. Both are instrumental in changing Utah’s formerly representative system: Meet Marc Tucker and Deborah Quazzo.

MARC TUCKER, THE SOCIALIST
To know Marc Tucker, simply peruse his report on Governing American Education, which says: “And the United States will have to largely abandon the beloved emblem of American education: local control... much of the new authority will have to come at the expense of local control.”
You can also study his infamous 1992 letter to Hillary Clinton, which was made part of the U.S. Congressional Record. The letter outlined Tucker’s vision of a communist-styled pipeline of education and workforce that would control individuals from early childhood through life.
It is a vision indistinguishable from Communism. It is a vision that Dabakis’ SJR16 consummates.
Tucker was invited recently by Utah legislators to speak in Utah at a statewide joint legislative/school board/USOE conference held at Southern Utah University. He’s also spoken at countless national venues, some of which are radical left-wing institutions: the Annenberg Institute, the Public Education and Business Coalition, the Aspen Institute, and state education conferences in various states.

DEBORAH QUAZZO, CORPORATE HOG
Less that a year ago, Salt Lake City sponsored an education-tech conference co-hosted by GSV Advisors (an investment group) with Arizona State University. Bill Gates paid for it, of course. Former USDOE Secretary Arne Duncan was a featured speaker. Ms. Deborah Quazzo, founder and CEO of GSV Advisors, headed the conference, and was listed as “a prolific angel investor” who “leverages technology in the global $4.9 trillion education and talent technology sectors”.
She charged people $2,795 per person to attend this conference– just to walk in the door.
Above, you saw the graphic of Quazzo’s “Strategic Battle Plan” for GSV (and Utah politics). Keep in mind that Quazzo is an investor, not an educator. Her battle plan has nothing to do with what you or I as teachers and parents know is best for our children. It is her openly, repeatedly stated desire to eliminate local control by eliminating elected school boards.
[As an aside, here is some context: Forbes christened Salt Lake City the “tech mecca” of America, so now, ambitious, hungry eyes are on Utah’s ed-tech industry and school system and taxpayers’ votes. Those hungry eyes care deeply about whether Dabakis’ bill passes. From their point of view, voters and teachers and parents and children are a necessary annoyance, but they feel that our elected school boards are not: so, if Utah eliminates “messy” debate and gets rid of the old time-consuming elected representation business; if Utah streamlines decision-making for the entire state, we will have created an ed-tech dictatorship. It’s so very profitable to those (inside and outside Utah) who invest in the Common Core-aligned education system that Tucker and Quazzo promote. If it’s hard to wrap your brain around socialism now bedding with corporate America, or of socialism taking over the Utah legislature, just revisit how this “elimination of boards” policy –espoused by the GSV investment group that is repeatedly in our state preaching to legislators– perfectly matches the communist “human capital pipeline” agenda of Marc Tucker. Utah’s not utterly clueless, either; remember that Tucker and Quazzo were invited to this state to advise the once conservative legislators and businesses of Utah.]
How many mecca attendees last spring had read Quazzo’s creepy GSV document, entitled American Revolution 2.0, which echoes Tucker’s call for the removal of local control and local school boards? How many agree with it now– other than virtually the entire Utah Senate? The GSV calls for the promotion of Common Core and the elimination of elected school boards. What a strange coincidence that the Tucker-featured SUU conference also called for the same things.
In the GSV document’s “Strategic Battle Plan” Quazzo and company say: “We eliminate locally elected school boards, recognizing that the process by which they are elected doesn’t correspond with either strategic planning or longer term results.”
Strategic planning for whom? Longer term results for whom? WHAT ABOUT THE CHILDREN? And what about the taxpaying voters who are to foot the bill without a voice in it? What about the reasons we fought the American Revolution 1.0? We wanted representation. We wanted a voice in our own lives, not dicatorship by Mother England. Do we want a dictatorship led by Mother Quazzo or Mother Dickson or Father Gates?
This bill of Dabakis, the consummation of Quazzo’s and Tucker’s long-term scheming, must be stopped.
Please, please, please contact the Utah House of Representatives immediately.
Immediately!
https://house.utah.gov/house-members/
UTAH STATE REPS:
bgreene@le.utah.gov
mroberts@le.utah.gov
mike@utahlegalteam.com
anderegg.jake@gmail.com
ssandall@le.utah.gov
jeffersonrmoss@gmail.com
jeffersonmoss@le.utah.gov
valpotter@le.utah.gov
curtwebb@le.utah.gov
eredd@le.utah.gov
justinfawson@le.utah.gov
corymaloy@le.utah.gov
sbarlow@le.utah.gov
gfroerer@le.utah.gov
vpeterson@le.utah.gov
jeremyapeterson@le.utah.gov
dpitcher@utah.gov
kmiles@le.utah.gov
pray@utah.gov
mikeschultz@le.utah.gov
karilisonbee@le.utah.gov
bradwilson@utah.gov
stevehandy@utah.gov
thawkes@le.utah.gov
beckyedwards@le.utah.gov
dougsagers@le.utah.gov
rayward@le.utah.gov
sduckworth@le.utah.gov
shollins@le.utah.gov
rchouck@le.utah.gov
jbriscoe@le.utah.gov
angelaromero@le.utah.gov
briansking@le.utah.gov
leeperry@le.utah.gov
mikewinder@le.utah.gov
lavarchristensen@le.utah.gov
elizabethweight@le.utah.gov
chall@le.utah.gov
kkwan@le.utah.gov
parent@le.utah.gov
markwheatley@le.utah.gov
csmoss@le.utah.gov
ehutchings@utah.gov
jdunnigan@utah.gov
lhemingway@le.utah.gov
kimcoleman@le.utah.gov
cacton@le.utah.gov
seliason@le.utah.gov
mariepoulson@le.utah.gov
kstratton@le.utah.gov
rspendlove@le.utah.gov
greghughes@le.utah.gov
jknotwell@le.utah.gov
susanpulsipher@le.utah.gov
loganwilde@le.utah.gov
tquinn@le.utah.gov
scottchew@le.utah.gov
kchristofferson@le.utah.gov
derrinowens@le.utah.gov
brad@braddaw.com
keithgrover@le.utah.gov
tseegmiller@le.utah.gov
adamrobertson@le.utah.gov
normthurston64@gmail.com
fgibson@le.utah.gov,
mnelson@le.utah.gov
christinewatkins@le.utah.gov
carlalbrecht@le.utah.gov
blast@le.utah.gov
jwestwood@le.utah.gov
vlsnow@le.utah.gov
mnoel@kanab.net
wbrooks@le.utah.gov
UTAH STATE SENATORS:
lescamilla@le.utah.gov dipson@le.utah.gov,
evickers@le.utah.gov,
dhinkins@le.utah.gov
kvantassell@le.utah.gov
lhillyard@le.utah.gov
rokerlund@le.utah.gov
tweiler@le.utah.gov
jsadams@le.utah.gov
hstephenson@le.utah.gov,
jwstevenson@le.utah.gov,
achristensen@le.utah.gov,
gbuxton@le.utah.gov
pknudson@le.utah.gov, curt@cbramble.com
mdayton@le.utah.gov
janderegg@le.utah.gov
dthatcher@le.utah.gov
dhemmert@le.utah.gov
wniederhauser@le.utah.gov
lfillmore@le.utah.gov
bzehnder@le.utah.gov
dhenderson@le.utah.gov
wharper@le.utah.gov
kmayne@le.utah.gov
jiwamoto@le.utah.gov
gdavis@le.utah.gov
–and our endangered state school board:
Board@schools.utah.gov


The following is authored by former US Congressman Bob Schaffer and is posted with his permission. In light of the fact that Marc Tucker has been invited to advise the Utah legislature on education at this week’s two day education conference, it seemed important to remember the history behind the changes that are culminating now, which Tucker and Hillary Clinton detailed in motion in the 1990s. Thanks to Bob Schaffer for his timely update.
_________________________________________________________
Thanks Christel:
I am grateful for your inquiry and certainly wish you well in your patriotic efforts in Utah. Incidentally, your readers can find PDF files of each page of Marc Tucker’s “Dear Hillary” letter in the 1998 Congressional Record through these links: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7.
The “Dear Hillary” letter is as relevant today as it was in 1992. Though I doubt anyone in the halls of government much remembers the letter itself, it is the concise, clear, and intentional nature of the letter that is instructive to those of us who still find value in the idea of a constitutional republic self-governed by free and intelligent citizens. Tucker’s sweeping 1992 blueprint for nationalizing the American public-education system is especially pertinent now because, at least since the day it was penned, it has been brilliantly executed with virtually no deviation.
It is instructive to note Tucker’s blueprint does not stop at nationalizing primary public education. It entails merging nationalized primary-education goals with a nationalized higher-education system and a nationalized labor-administrative function. Think of the 1990s doublespeak “School-to-Work” and you get an accurate picture. School-to-Work, as you know, was the apt title of the Clinton-era initiative setting the Tucker letter into actual national public policy. More practically, think of the “Prussian-German, education-labor model” because it is the same thing. Tucker actually says so in the letter itself: “We propose that (President-elect) Bill take a leaf out of the German book.”
Truly, Tucker’s ideas are not new. They were formalized by Jean-Jacques Rousseau, refined by Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, embedded by Hegel in the German university structure, then exported throughout the world including to virtually every “teachers college” in America. Specific to the perpetual, anti-intellectual quest to undermine the traditions of “classical” education, Rousseau’s “social-contract” ideas (wherein individuals are understood as subordinate to state interests and royal continuity) were perfected for European classrooms by heralded social engineers such as Heinrich Pestalozzi and Friedrich Froebel. These ideas were most powerfully applied to American classrooms by John Dewey. Despite being deeply embedded in the curriculum of modern American teacher’s colleges, these collectivist ideals and progressive-romantic philosophies have been held in marginal abeyance by the brilliant American design of decentralized, independent, sovereign states each in charge of its own public-education system.
Accordingly, this is where Tucker’s “Dear Hillary” letter earns its notorious repute. An acolyte of the worn Rousseau-Dewey, progressive-romantic line of thinking, Tucker eloquently maps in his 1992 letter to the new First Lady a sharp and detailed political plan for mutating American primary education, secondary education, and labor policy in ways that can breach the pesky firewalls of the Tenth Amendment if not the core revolutionary ideal of federalism itself. Hegel would have been elated. Dewey’s, Pestalozzi’s, and Froebel’s names are already painted on the ceiling of the Library of Congress – main floor, at that.
Though eight years of the Clinton administration have come and gone (maybe), the tactics of the “Dear Hillary” letter roll onward. Not a single manifestation of “Dear Hillary” policies was curtailed during the Bush presidency. In fact, many were accelerated through “No Child Left Behind.” The Obama administration has effectuated “Dear Hillary” objectives to nearly complete fruition.
As to your curiosity about why I petitioned the House of Representatives in 1998 to allow me to preserve the Tucker letter as I did, my best explanation follows.
After discovering, studying and digesting the transformational implications of the “Dear Hillary” letter, and concluding it carried credible political heft, I thought it important to enshrine the missive via The Congressional Record perhaps as a self-explanatory and incontrovertible marker as to whom, when, where and how the United States of America finally and completely disconnected itself from the proven ideals of classical education – the kind of education the country’s Founders received. As a youngish, backbench first-term Member of Congress in 1998, I thought someday maybe someone working on a Master’s thesis would like to pinpoint the moment our former republic opted instead for the amply disproven, constrained and anti-intellectual objectives of formalized “training.” Maybe my Congressional-Record entry would be of good use to an aspiring scholar or two.
Indeed, history is replete with examples of classical education leading to strong, powerful individuals; and formalized training leading to a strong, powerful state. I regarded this letter as a signal of an epic American turning point. I actually did imagine the letter would one day be regarded as an important historic document worthy of being singled out and remembered. I maintain that belief even now, and am delighted you are among those who recognize its significance.
It seemed to me at the time, the “Dear Hillary” letter was the most concise, honest and transparent political document of its kind. It reminded me of the moment Gen. George McClelland at Sharpsburg came into possession of Gen. Robert Lee’s plans for an offensive at Antietam Creek. Here in these plans, one actually reads a credible battle strategy for overcoming American federalism. Tucker’s war cannons were fully charged and tightly packed with progressive-romantic canister, aimed directly upon the Founder’s revolutionary idea of republican, self-government and our traditions of states’ rights.
I had anticipated my colleagues in the Congress and various state-education leaders would benefit from knowing, in advance, of Tucker’s offensive strategy especially as his battle plan was specifically addressed to, and received by, the occupants of the White House. The last thing I ever imagined at the time (and I am heartbroken to realize it now), is how political leaders in the several states have stood indolently for it. Never did I picture the baleful scene we are witnessing today – state leaders themselves dutifully lowering Tucker’s linstock to the touch hole of statism.
At least for the past couple of decades, the vast majority of elected leaders in both political parties have clearly – if not enthusiastically – worked to outdo one another in applying Rousseau-Hegel-Dewey ideas to public education. They offer little, if any, impressive resistance to policies, laws, rules, and mandates relegating American education to a job-training enterprise despite the prescient warnings of Albert Jay Nock, E.D. Hirsch, Tracy Lee Simmons and others who have underscored the crucial difference between classical education and anti-intellectual training. As such, Tucker’s letter and goals, though overtly political, cannot be fairly regarded as a partisan. No, the epic transformation of American culture and national character is being achieved rather quickly due to an overwhelming advantage of spectacular bipartisan cooperation.
Henceforward, when intelligent people scratch their heads and wonder how it was that the citizens of the United State of America inexplicably stood by and unwittingly participated in the systematic demise of their blessed republic, at least they’ll find one comprehensive and compelling explanation, assuming it survives the censors’ notice, in The Congressional Record on September 25, 1998.
Thank you for finding me, reaching out to me, and granting me an opportunity to underscore the perilous certainties of the country’s education system.
Very truly yours,
Bob Schaffer
—————
On a related note, I invite the officials who will be participating in so-called “guided” discussions at this week’s conference to truly arm themselves against the manipulative “delphi technique” that is used to force consensus, as outlined by Jenny Hatch here.
I’m surely sprouting new gray hairs at 80 miles per hour.
If there was doubt about whether something was truly rotten in the state of education governance here in sweet, naiive Utah, this news should end that doubt: of all the possible gurus, this is who our legislators, USOE and state school board have invited as the out-of-town centerpiece for a joint education conference taking place this Wednesday and Thursday.

Marc Tucker.
You may recall that he’s on the Top Ten List of Scariest People in Education Reform.
He’s the espouser of no more Algebra II in our high schools, the dismisser of classic literature as not so relevant, a disciple of federal power, a conspirator with Hillary Clinton for cradle-to-grave student-citizen micromanagement, and the top crusader against what he calls “the beloved American emblem: local control” –he’s the one.
The conference is for Utah’s State Board of Education, State Office of Education, and legislators, but it’s open to the public and will be streamed.
If you can attend, it’s on September 2 and 3, at Gilbert Great Hall, R. Haze Hunter Conference Center, Southern Utah University, Cedar City, Utah.

If you don’t know who Marc Tucker is, learn a little bit more.
Marc Tucker is– unbelievable as it may seem– an open advocate for the complete deletion of local control. You read it right. This is a direct quote from Tucker:
The United States will have to largely abandon the beloved emblem of American education: local control. If the goal is to greatly increase the capacity and authority of the state education agencies, much of the new authority will have to come at the expense of local control.
Marc Tucker also despises what is –or was– real education, in favor of the robotic efficiency of cradle-to-grave federal micromanagement of systems. He wrote the unbelievable NCEE report that advocates for the removal of Algebra II –and any math beyond it from high schools, that also labeled classic literature and student personal writing “less relevant” and dismissable. If this sounds like impossible, deliberate dumbing down, you have not read Tucker’s reasoning, which envisions a socialist’s factory view of school: a place to create economy-centered worker bees, to generate a collective; not a place to “waste” resources for soaring and free thinkers. He’s all about efficiency at the expense of individual freedom.
Marc Tucker’s BFF relationship with the creepiest lady in D.C., Hillary Clinton, is notable. It is a decades-long collaboration that, back in the 90s, envisioned US education with all federal control rather than any local control. That collaboration was recorded in the Congressional public record. Tucker and Clinton outlined the entire Common Core/Common Data movement, but used different terminology. Read that in full sometime.
Marc Tucker’s shameful, anti-freedom philosophies have been repeatedly, successfully put to pasture by great thinkers and scholars– for example, very clearly, by Dr. Yong Zhao. Dr. Zhao should have been invited to advise Utah this week, not Tucker!
If you want to know more, I’ve written many articles about Marc Tucker. He’s bad news. Read my archive on Tucker at this link.
I really can’t believe he’s coming.
What are your thoughts? Is this okay?

–If he were invited to the university for a two-sided debate, fine!
–If his visit was a University lecture, some attempt by the dean to expose students to radical ideas from extreme ends of a spectrum, fine!
But this is not a university lecture.
It’s a joint legislative – school board – USOE meeting, which just happens to be taking place at SUU. It could have been at any venue.
No one is slated to debate him.
Marc “end-local-control” Tucker is the only out of town speaker coming to this conference to address the Utah legislature and the Utah State Office and School Board. He was hand selected for the at-taxpayer-expense conference –as someone to look to for advice.
That decision says more about the state of education politics in Utah than anything more I could write tonight.

Top Ten Scariest People in Education Reform:
#3
Marc Tucker, President of National Center on Education and the Economy

Countdown # 3
This is the seventh in a countdown series of introductions, a list of the top ten scariest people leading education in America. For number 4, number 5, number 6, number 7, number 8, number 9 and number 10, click here.
Just like like the others on this Top Ten list, Marc Tucker comes across as a nice guy; he carries no pitchfork, wears no horns, debates politely.
Yet Marc Tucker has openly worked for decades to “strengthen the role of the state education agencies in education governance at the expense of “local control” and insists that “the United States will have to largely abandon the beloved emblem of American education: local control.” (See links below.) He wants to alter the actual quality of U.S. education, also. For example, he hopes to remove “the policy of requiring a passing score on an Algebra II exam for high school graduation” because he feels that overeducating the masses is a waste of collective tax money.
These goals and others are published by Tucker at the National Center on Education and the Economy (NCEE) and the Center for American Progress. The NCEE, the organization over which he presides, is paid millions to promote these damaging ideas by Common Core main-funder Bill Gates.
Tucker’s ideas have garnered widespread acceptance. He speaks at countless education conferences; for example, he’s spoken at the Annenberg Institute, the Public Education and Business Coalition, at Kentucky’s Conference on the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, the Aspen Institute, at numerous colleges and universities and has testified to state legislatures about education.
And these ideas are nothing new. In Tucker’s infamous 1992 letter to Hillary Clinton, now part of the Congressional Record, he outlined his vision of a communist-styled pipeline of education and workforce that would control individuals from early childhood through workforce. He and Hillary shared the vision: “to remold the entire American system for human resources development… This is interwoven with a new approach to governing… What is essential is that we create a seamless web… from cradle to grave and is the same system for everyone — young and old, poor and rich, worker and full-time student. It needs to be a system… guided by clear standards… regulated on the basis of outcomes…”
Can anyone distinguish between that Tucker quote and actual, literal Communism for me? I see no difference.
That was in 1992. It seemed conspiratorial at that time. But it’s openly pursued today by Tucker and by his associates on the Top Ten Scariest list).
Fast forward to 2007.
In a report entitled “Tough Choices for Tough Times” Tucker’s NCEE implied that America had the constitutional authority, and suggested that America should: develop national standards, tests and curriculum; create “personal competitiveness accounts,”should “create regional competitveness authorities,” should provide “universal early childhood education,” should tie teacher evaluation to teacher pay, and more. Remember, Common Core national standards weren’t adopted by the majority of states (or even offered via the Race to the Top grant) until 2009-2010. But Tucker had this going on long ago.
Fast forward to 2013.
The Center for American Progress published this report in which Tucker asserted, among other things, that “the United States will have to largely abandon the beloved emblem of American education: local control.”

Here’s a little taste of what his report proposed:

If Americans are going to decide which level of government we want to run our education systems, the only realistic choice is the state. No one wants a national education system run by the federal government, and the districts cannot play that role. [Why wouldn’t local school districts serve in that controlling role? –Too “we the people” for Mr. Tucker, perhaps?]
…Each state needs to consolidate in its state department of education the policymaking and implementation authority that now resides in a welter of state-level commissions, agencies, and other independent bodies. And the United States will have to largely abandon the beloved emblem of American education: local control. If the goal is to greatly increase the capacity and authority of the state education agencies, much of the new authority will have to come at the expense of local control.
….I propose to greatly strengthen the role of the state education agencies in education governance, at the expense of “local control…” The line of political accountability would run to mayors and governors through their appointees… governance of the schools, higher education, early child- hood education and youth services would all be closely coordinated through the governance system… I propose that a new National Governing Council on Education be established, composed of representatives of the states and of the federal government, to create the appropriate bodies…”
Did Tucker really think that “we, the people” would roll over and give in to his constitution-slaughtering dream to end local control and to permit governmental tyranny over education?
Don’t go refill your soda yet. There’s more.
In 2013, Marc Tucker also put out this document at the National Center on Education and the Economy, that says out loud that it’s not important under Common Core to have high educational standards in high school; that it’s silly to waste time educating all high school graduates as high as the level of Algebra II.
Tucker thus pushed for an emphasis on the lowest common denominator, while also marketing Common Core as a push for “rigorous” academics.
Read for yourself:
“Mastery of Algebra II is widely thought to be a prerequisite for success in college and careers. Our research shows that that is not so… Based on our data, one cannot make the case that high school graduates must be proficient in Algebra II to be ready for college and careers. The high school mathematics curriculum is now centered on the teaching of a sequence of courses leading to calculus that includes Geometry, Algebra II, Pre-Calculus and Calculus. However, fewer than five percent of American workers and an even smaller percentage of community college students will ever need to master the courses in this sequence in their college or in the workplace… they should not be required courses in our high schools. To require these courses in high school is to deny to many students the opportunity to graduate high school because they have not mastered a sequence of mathematics courses they will never need. In the face of these findings, the policy of requiring a passing score on an Algebra II exam for high school graduation simply cannot be justified.”
So, Tucker’s NCEE report goes on to say that traditional high school English classes, with their emphasis on classic literature and personal, narrative writing, is useless. The report says that Common Core will save students from the worthless classics with its emphasis on technical subjects and social studies via the dominance of informational text in the Common Core classroom:
“The Common Core State Standards in English Language Arts (CCSSE) address reading in history/social studies as well as science and technical subjects, and in so doing may increase the relevance of high school instruction.”
Did you catch that? Tucker and the NCEE just trashed English literature, calling it irrelevant. And, in calling classic literature and personal writing irrelevant, he underscores the socialist mentality: that only job prep matters, only the collective economy, not the mind and soul of the individual.
In 2014, Marc Tucker wrote an article entitled “On Writing” in which he suggested the country should “hold our teachers accountable for the quality of student writing” –saying that incentivizing teachers would increase college level literacy. (To Tucker, teachers and students seem to be lab rats. Hand out larger government chunks of cheese and the rats will do whatever you like.)
Teacher Mercedes Schneider shredded Tucker’s “On Writing” arguments here. Sandra Stotsky, Cherilyn Eagar , Diane Ravitch, Paul Horton and Susan Ohanian have written important points about Marc Tucker as well.
Lastly, for those who follow the money trail: Marc Tucker and his NCEE have accepted many millions from Common Core-builder/funder Bill Gates. So has the Tucker-publishing, CommonCore – friendly Center for American Progress.

Dr. Sandra Stotsky, one of the famous Common Core validation committee members who refused to sign off on the legitimacy of Common Core, is alarmed that N.H. legislators are being sold a false line by Mark Tucker about Common Core. She points out, among other things, that the Gates Foundation has “given millions to help Marc Tucker promote his own ideas on education in recent years” as it has given millions to promote Common Core nationwide. But there are more than financial incentives for Tucker, the CEO of the National Center on Education and the Economy (NCEE), a Center for American Progress (CAP) leader, and the infamous Dear Hillary letter author.
Tucker’s life’s work hangs on Common Core. He’s made it his mission to end local control, as a progressive socialist who openly fights Constitutional, representative America. The plot of his 1992 “Dear Hillary letter” falls apart without Common standards for control of data and control of education and workforce. He can’t let it fail.
Tucker’s infamous 1992 letter to Hillary Clinton showed Tucker’s (and Clinton’s) twisted agreement that a “new” system of government should micromanage every citizen’s life, cradle to grave, using schooling as the core for the centralized control. Creepy as can be.
Fast forward to May 2013 and still, you see Tucker’s creepy goals outlined in his report from the “Center for American Progress” in which Tucker stated that “the United States will have to largely abandon the beloved emblem of American education: local control.” He also dared write: “I propose to greatly strengthen the role of the state education agencies in education governance, at the expense of local control … [G]overnance roles of the local districts, as well as the federal government, would be significantly decreased. Independent citizen governing boards would be eliminated.”

Equally stunning is Tucker’s 2013 NCEE report called “What Does It Really Mean to Be College and Work Ready?” where he admitted that his goal for education reform is NOT to raise, but to lower standards.
His report reads:
“Mastery of Algebra II is widely thought to be a prerequisite for success in college and careers. Our research shows that that is not so… Based on our data, one cannot make the case that high school graduates must be proficient in Algebra II to be ready for college and careers… the policy of requiring a passing score on an Algebra II exam for high school graduation simply cannot be justified.”
(Why don’t our state school boards share these reports with us? Why do they lead us to believe that “college and career ready standards” mean better than we had before?)
The same NCEE report goes on to say that the traditional high school English class, with its emphasis on classic literature and personal, narrative writing, is useless. The report implies that Common Core will save students from the near-worthless classics with its emphasis on technical subjects and social studies via the dominance of informational text in the Common Core classroom:
“The Common Core State Standards in English Language Arts (CCSSE) address reading in history/social studies as well as science and technical subjects, and in so doing may increase the relevance of high school instruction.”
In labeling classic literature and personal writing irrelevant, the NCEE underscores the Common Core/NCEE mentality: that only job prep matters, only the collective economy, not the liberty and potential of an individual.
With that introduction to Tucker’s motivations for promoting Common Core, here are highlights from Dr. Stotsky’s article on Tucker’s recent fibs in support of the Common Core agenda. (Read the whole thing at Pioneer Institute’s website.)

Dr. Stotsky makes many important points, including the following:
1 “In October, members of the New Hampshire legislature heard Marc Tucker, president of the National Center on Education and the Economy, tell them more fibs than Pinocchio ever dreamed up. How many legislators will prove to be gullible Geppettos is another matter.”
2 “…all six of the “math experts” who “validated” Common Core’s mathematics standards are in an education school and/or spend their time on teacher education… [Dr. James Milgram, who refused to sign off on the legitimacy of the Common Core math standards], who has a doctorate in mathematics, was clearly the only mathematician on the Validation Committee. Tucker doesn’t know a mathematician from a mathematics educator.”
3 “It is true that Professor William McCallum, a consultant to Achieve, Inc., a mathematics professor at Arizona State University, and a lead writer of Common Core’s mathematics standards, asked the heads of many national mathematics and science societies for endorsements, and he received them. However, there is no evidence that any of their members ever read Common Core’s high school mathematics standards.”
4 “Nor is there evidence that any of their members disagree with Milgram’s judgment that there are no precalculus standards in Common Core or with Professor Jason Zimba’s acknowledgment that Common Core does not prepare high school students for STEM. If members of these organizations do endorse high school mathematics standards that intentionally do not prepare high school students for STEM, they should speak up…”
5 “Mitchell Chester, current Commissioner of Education in Massachusetts, did not commission any leading education research organizations to compare the Massachusetts standards with Common Core’s …Achieve, Inc., Fordham, and the MBAE all received funding from the Gates Foundation… It is also well-known that a Race to the Top grant for $250,000,000 was promised to Massachusetts if it adopted Common Core’s standards.”
6 “Tucker plays fast and loose with the facts, and in the future New Hampshire legislators and educators should make sure a fact-checker is on the premises for a debriefing after he speaks.”
Thank you, Dr. Stotsky.
Read the rest here.
Thomas Jefferson wrote: “But if it is believed that these elementary schools will be better managed by the governor and council, the commissioners of the literary fund, or any other general authority of the government, than by the parents within each ward, it is a belief against all experience.“
America, do we you want that sterile, big-government factory vision of workforce-focus to control the nation’s children? How has it worked out for European socialist countries and the communist nations?
Why listen to Tucker and go with his (Common Core’s) flow? Why destroy the vision of our founders, where each caring parent and locality governed the child’s education?
Local control and freedom have made us the greatest nation in the world. Others flock to our universities! Others envy our technological and medical advancement!
Freedom works. Don’t throw it away, foolishly following schemers such as Marc Tucker, David Coleman, Sir Michael Barber, Bill Gates, and Arne Duncan –no matter how fancy the titles of their organizations sound.
We’re at a critical intersection of our country’s history. Our children’s futures and our country’s future depends on us seeing what these schemers are attempting to pull; depends on us standing up and simply saying, “No.”
Subservience to truly stupid ideas —like dumbing down high school math for economic gain— was never meant to be the destiny of the free American people.
Yet that is what has happened to American education under Common Core. In the video testimony of Common Core creator Jason Zimba, in recent articles by the American Institutes for Research (AIR), in the written testimony of Common Core validation members Dr. Sandra Stotsky and Dr. James Milgram, and in the 2013 Common Core report of the National Center for Education and the Economy (NCEE) we see that Common Core math deliberately diminishes and weakens, rather than adding to, high school math standards.
At the American Institutes for Research (AIR) website, (FYI, this is the company that writes Utah’s Common Core math and English test) there are articles claiming that it’s in the best interest of the taxpayers that more students should only aim for a two year college degree.
AIR dismisses the idea that a student might WANT to learn more than what is available at the associates’ degree level. Individual desires and rights don’t even factor into the collectivism of education reform.
AIR fails to address the fact that not all college educations are tax-funded; some people actually pay for their own tuition. AIR takes the socialist view that taxpayers are “stakeholders” so they should determine whether a student may or may not get more education. AIR says: “Do graduates who earn an associate’s degree and participate in the labor force experience returns, such as higher wages, that justify the costs incurred by them in obtaining that degree? Do taxpayers receive a positive return on their investment in the production of associate’s degrees?”

Professor Sandra Stotsky, who served on the official Common Core Validation Committee, has written an article, Common Core Math Standards Do Not Prepare U.S. Students for STEM Careers. How Come?” (It is posted in full at Heritage Foundation’s website.)
Dr. Stotsky writes that states adopted Common Core math because they were told that it would make high school students “college- and career-ready” and would strengthen the pipeline for science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), but it is clear this claim was not true. Stotsky reminds us that Professor James Milgram has testified to the fact that common core math dumbed down U.S. high school standards.

James Milgram
With the exception of a few standards in trigonometry, the math standards END after Algebra II, reported Stanford emeritus professor James Milgram (Milgram was also an official member of the Common Core validation committee.)
Both Milgram and Stotsky refused to sign off on the academic quality of the national standards, and made public their explanation and criticism of the final version of Common Core’s standards.
Stotsky points out that the lead mathematics standards writers themselves were telling the public how LOW Common Core’s high school math standards were. At a March 2010 meeting of the Massachusetts Board of Elementary and Secondary Education, Jason Zimba, a lead writer, told the board that the standards are “not only not for STEM, they are also not for selective colleges.”
Yet, strangely, Stotsky was the only member of the board who expressed concern upon hearing Zimba’s words. Watch that one minute video here.
Stotsky explains:
“U.S. government data show that only one out of every 50 prospective STEM majors who begin their undergraduate math coursework at the precalculus level or lower will earn bachelor’s degrees in a STEM area. Moreover, students whose last high school mathematics course was Algebra II or lower have less than a 40 percent chance of earning any kind of four-year college degree.”
Not only that: Stotsky points out that in January 2010, William McCallum, another lead mathematics standards writer, told a group of mathematicians: “The overall standards would not be too high, certainly not in comparison [to] other nations, including East Asia, where math education excels.”
Dr. Stotsky also notes that there are “other consequences to over 46 states having a college readiness test with low expectations.” The U.S. Department of Education’s competitive grant program, Race to the Top, required states to place students who have been admitted by their public colleges and universities into credit-bearing (non-remedial) mathematics (and English) courses if they have passed a Common Core–based “college readiness” test. Stotsky writes: “Selective public colleges and universities will likely have to lower the level of their introductory math courses to avoid unacceptably high failure rates.”
Stotsky says, “It is still astonishing that over 46 boards of education adopted Common Core’s standards—usually at the recommendation of their commissioner of education and department of education staff—without asking the faculty who teach mathematics and English at their own higher education institutions (and in their own high schools) to do an analysis of Common Core’s definition of college readiness… Who could be better judges of college readiness?”
Read the rest of Stotsky’s article here.
What about NCEE? Surely the National Center on Education and the Economy (NCEE) would not want to dumb down your child!
Sigh.
In the 2013 report from NCEE, “What Does It Really Mean to be College and Career Ready?” it recommends that we all throw out the higher math we used to teach in high schools in America.
“Mastery of Algebra II is widely thought to be a prerequisite for success in college and careers. Our research shows that that is not so… Based on our data, one cannot make the case that high school graduates must be proficient in Algebra II to be ready for college and careers. The high school mathematics curriculum is now centered on the teaching of a sequence of courses leading to calculus that includes Geometry, Algebra II, Pre-Calculus and Calculus. However, fewer than five percent of American workers and an even smaller percentage of community college students will ever need to master the courses in this sequence in their college or in the workplace… they should not be required courses in our high schools. To require these courses in high school is to deny to many students the opportunity to graduate high school because they have not mastered a sequence of mathematics courses they will never need. In the face of these findings, the policy of requiring a passing score on an Algebra II exam for high school graduation simply cannot be justified.”

Read the rest of the NCEE report here.
When will people stop saying that Common Core standards are legitimate preparation for 4 year colleges? It so obviously isn’t true.
When will people admit that Common Core caters to a low common denominator and robs high achievers and mid-achievers? Probably never. Proponents pushed Common Core on Americans for a deliberate purpose: so that politicians and the private corporations they’ve partnered with, can analyze, punish and reward those who have forgotten that they have real rights under a real Constitution to direct and control their own affairs.
———————————————————————————
Thank you, Dr. Sandra Stotsky and Dr. James Milgram for your tireless testimonies about American education reforms that hurt our children and our country.


There aren’t many people of whom you can correctly say that this person is a conspirator against the America we all know and cherish. But Marc Tucker fits into that category, indisputably.
(Evidence: His 1992 letter to Hillary Clinton, which was archived in the Congressional Record, showed his twisted vision of a new form of government that would micromanage every step of the citizens’ lives, using schooling as the facade for the control. Read it here.)
Marc Tucker’s been arguing his point in academic circles for a long time. He got a recent beating-up by the brilliant Professor Yong Zhao for his controllist ideas. But he doesn’t give up.
Marc Tucker has long been ambitious to break down all that represents freedom in education.
BUT NOW:
The Center for American Progress (which “progresses” America away from the Constitution) published this recent report in which Tucker asserts, among other things, that “the United States will have to largely abandon the beloved emblem of American education: local control.”

Here’s a little taste of what his report proposes:

If Americans are going to decide which level of government we want to run our education systems, the only realistic choice is the state. No one wants a national education system run by the federal government, and the districts cannot play that role.
[Mr. Tucker– why not? Why wouldn’t districts play that role? –Silly man.]
…Each state needs to consolidate in its state department of education the policymaking and implementation authority that now resides in a welter of state-level commissions, agencies, and other independent bodies. And the United States will have to largely abandon the beloved emblem of American education: local control. If the goal is to greatly increase the capacity and authority of the state education agencies, much of the new authority will have to come at the expense of local control.
….I propose to greatly strengthen the role of the state education agencies in education governance, at the expense of “local control,” and of the federal government. In this plan, school funding would be the responsibility of the state, not the locality, and the distribution of state funds for schools would have nothing to do with the distribution of local property wealth. Thus the governance roles of the local districts, as well as the federal government, would be significantly decreased. Independent citizen governing boards would be eliminated. The line of political accountability would run to mayors and governors through their appointees. At the state level, the governance of the schools, higher education, early child- hood education and youth services would all be closely coordinated through the governance system. Though the role of the federal government would be curtailed, there are some very important national functions that must be served in a modern education system. I propose that a new National Governing Council on Education be established, composed of representatives of the states and of the federal government, to create the appropriate bodies to oversee these functions…”
Did Tucker really think that WE THE PEOPLE were going to roll over and give in to his constitution-slaughtering dream to end local control and to permit governmental tyranny over education?
Really?
I believe that WE THE PEOPLE will stand up for our children.
Tucker’s 1992 socializing-America letter to Hillary may have partially come to pass. But he will not win this one. Because this time, we are awake.

Yong Zhao
It’s always fun to watch smart people debate an important topic, but it’s especially satisfying when the person whose side you are on wins the day. That is Yong Zhao, who seems to me not only smart but also wise.
Many are following the Marc Tucker/ Yong Zhao interchange about Common Core with great interest. http://zhaolearning.com/2013/01/17/more-questions-about-the-common-core-response-to-marc-tucker/

Marc Tucker
Marc Tucker is an old pal and co-conspirator with Hillary Clinton, and their written “Let’s Take Over American Education” exchange has long been archived in the Congressional Record, partially because of its conspiratorial nature. I’ve posted about it before: https://whatiscommoncore.wordpress.com/2012/06/22/anti-liberty-plot-for-american-education-full-text-of-the-letter-from-marc-tucker-to-hillary-clinton-2/
So, Tucker is no friend to educational freedom; Zhao is.
Here is almost the whole of the latest brilliant response to Tucker by Yong Zhao. Full text here: http://zhaolearning.com/2013/01/17/more-questions-about-the-common-core-response-to-marc-tucker/
More Questions about the Common Core: Response to Marc Tucker
17 January 2013
…It is impossible, unnecessary, and harmful for a small group of individuals to predetermine and impose upon all students the same set of knowledge and skills and expect all students progress at the same pace (if the students don’t, it is the teachers’ and schools’ fault).
I am not against standards per se for good standards can serve as a useful guide. What I am against is Common and Core, that is, the same standards for all students and a few subjects (currently math and English language arts) as the core of all children’s education diet. I might even love the Common Core if they were not common or core.
Tucker disagrees. He argues it is both possible and necessary to predetermine and impose upon all students the same knowledge and skills and America is immune to the damages of such efforts that have been experienced in China and other similar East Asian countries.
Now response to Tucker’s arguments point by point.
Tucker: It is now more important than ever to figure out what all young people need to know and be able to do.
Zhao: First, it is not true that “it is now more important than ever to figure out what all young people need to know and be able to do.” Over a hundred and fifty years ago, the British philosopher Herbert Spencer thought it was so important to decide what children should learn that he wrote the essay What Knowledge is of Most Worth and came up with the answer “science” and his criteria was the utilitarian value of knowledge. He did not think Latin, Greek, and the classics were of much value for a person to live in a society being transformed by industrialization and history , to Spencer was “mere tissue of names and dates and dead unmeaning events…it has not the remotest bearings on any our actions.”
In 1892, the National Education Association (NEA) thought it was so important that it appointed the Committee of Ten, chaired by Harvard president Charles Elliot, to figure out what schools should teach.
In early 1900s, The NEA had another commission to rethink the curriculum and came up with The Cardinal Principals of Secondary Education
Activities intended to determine what all students should know and be able to do never actually stopped. In recent years, the 1994 Goals 2000 Act under President Clinton provided funds to develop standards that “identify what all students should know and be able to do to live and work in the 21st century.” Under NCLB, states were mandated to develop both content and academic achievement standards in reading/language arts, mathematics, and science.
There has never been a lack of attempts to figure out what all young people should know and be able to do, consequently there is no shortage of standards around. The fact that there have been so many attempts suggests the difficulty of the task. People simply cannot seem to agree what all children should know and learn in general. People cannot even agree what to teach in math, the supposedly the most straightforward, and have fought many math wars over the last century. It is actually a good thing, in my mind, that people cannot come to agreement and the American federal government was not given the authority to impose its own version upon all children. But despite the lack of a consistently implemented nationalized curriculum and standards, America did just fine as a nation.
The Common Core initiative seems to suggest that either there are no standards in America or the existing standards are not good enough. But what evidence is there to show the Common Core is better than previous ones, including those from all 50 states? Granted that things change and what students learn should reflect the changes, but how frequently should that happen? The state standards developed under NCLB are merely a decade old. If we have to make massive changes every five or 10 years, does not it mean it is nearly impossible to come up with content that is valid long enough for the nation’s over 100,000 schools to implement before it becomes outdated? If so, would it be much more likely that individual schools and teachers have a better chance to make the adjustment faster than large bureaucracies?
An anecdote: For hundreds of years it was possible for the adults in my little village in China to figure out what all children should know and be able to do: handling the water buffalo was one for the boys and sewing for the girls. My village was small and isolated, with around 200 people. But that predication became invalid when China opened up to the outside world in the 1980s. The common standards in my village proved to be wrong later in at least two cases. First it did not work for me. I was pretty bad at what my village’s Common Core prescribed (handling the water buffalo) so I had to do something else (coming to America to debate with Marc Tucker, for example). Second, it did not work for the rest of the children in the village either, because working as a migrant worker in the city is different from handling a water buffalo.
Tucker: Truly creative people know a lot and they have worked hard at learning it. They typically know a lot about unrelated things and their creativity comes from putting those unrelated things together in unusual ways. Learning almost anything really well depends on mastering the conceptual structure of the underlying disciplines, because, without that scaffolding, we are not able to put new information and skills to work.
Zhao: Very true, truly creative people know a lot and they have worked hard at learning it, but do they know a lot about what they are passionate about, or what the government wants them to know? Do they work hard at learning something that is personally meaningful, or do they work hard at learning something prescribed by others?
Also true that learning anything really well depends on mastering the conceptual structure of the underlying disciplines, but what disciplines: math, science, the arts, music, languages, or politics? I am embarrassed to admit as a Chinese, I had horrible math scores in school, which is why I chose to study English, but somehow I am good at computer programming and developed large-scale software. I am also good at understanding statistics and empirical evidence.
Tucker: Zhao says that we will not be competitive simply by producing a nation of good test takers. That is, of course, true. Leading Asian educators are very much afraid that they have succeeded in producing good test takers who are not going to be very good at inventing the future. But that does not absolve us of the responsibility for figuring out what all students will need to know to be competitive in a highly competitive global labor market, nor does it absolve us of the responsibility to figure out how to assess the skills we think are most important.
Zhao: Is it responsibility or arrogance? Almost all totalitarian governments and dictators claim that they have the responsibility to engineer a society so their people can live happily and that their people are not capable of knowing what is good for them and top-level design is necessary. For example, they claim that their people cannot defend themselves against bad information, thus the leaders have to impose censorship. The leaders should decide what their people should view, listen to, and read. This self-assigned responsibility comes from the assumption that the authority knows best. By the way, we adults (parents and teachers) often committee the same error of arrogance: we automatically assume we know better than our children.
Tucker: It is true that the future will be full of jobs that do not exist now and challenges we cannot even imagine yet, never mind anticipate accurately. But, whatever those challenges turn out to be, I can guarantee you that they will not be met by people without strong quantitative skills, people who cannot construct a sound argument, people who know little of history or geography or economics, people who cannot write well.
Zhao: Almost true but strong quantitative skills are not the same as the skills to mark the right choice on a multiple choice exam, constructing a sound argument is different from repeating the “correct way” of arguing, and writing well certainly does not mean scoring high against a writing rubric. More importantly, as far as I can tell, the Common Core does not include what Tucker wants: history, geography, or economics. Where do the children learn these and other “unrelated things” when they are pushed aside by the Common Core?
Tucker: Zhao grew up in a country in which the aim was not learning but success on the test. There was wide agreement that the tests were deeply flawed, emphasizing what Mao called “stuffing the duck”— shoving facts and procedures into students—in lieu of analysis, synthesis and creativity. But few wanted to change the system, because the tests were one of the few incorruptible parts of a deeply corrupt system.
Zhao: Very good observation but I cannot help but pointing out that Tucker just published a book entitled Surpassing Shanghai: An Agenda for American Education Built on the World’s Leading Systems. If it is such a bad system, why does Tucker consider it one of the world’s leading systems and want to build American education on it? If it is so bad, what is it in Shanghai, a city of China, he wants America to surpass?
And by the way, it is not true that “few wanted to change the system, because the tests were one of the few incorruptible parts of a deeply corrupt system.” Many, perhaps, most people in China, want the system changed. The Ministry of Education and provincial governments have been making changes over the past few decades (for details read my books Catching Up or Leading the Way and World Class Learners)
Tucker: So Zhao is very much aware of the consequences of a rigid system set to outdated standards. But that is not the problem in the United States. We don’t suffer from ancient standards wildly out of tune with the times, enforced by tests that are no better. We suffer from lack of agreement on any standards that could define what all students must know and be able to do before they go their separate ways. We suffer in a great many schools from implicit standards that translate into abysmally low expectations for far too many students.
Zhao: I am very appreciative of Tucker’s understanding of my background but I am not convinced that the U.S. is immune to the same problems China has suffered from testing. Is it not the goal of the Common Core to instill a rigid system? Isn’t the Common Core to be enforced by tests? If not, why do we have the Common Assessment? Why are we connecting teacher evaluation to test scores? Moreover, haven’t we seen plenty of cases of cheating on standardized testing in our schools under NCLB? Isn’t there enough evidence of states manipulating data and cut scores? For more evidence, read Collateral Damage: How High-stakes Testing Corrupts America’s Schools by Sharon Nichols and David Berliner.
Another by the way: When I described the teacher evaluation efforts mandated by the Race to the Top to a group of science teachers from Beijing to study American science education this week, they were appalled and commented: Isn’t that a violation of human dignity?
Tucker: Without broad agreement on a well designed and internationally benchmarked system of standards, we have no hope of producing a nation of students who have the kind of skills, knowledge and creative capacities the nation so desperately needs. There is no substitute for spelling out what we think students everywhere should know and be able to do. Spelling it out is no guarantee that it will happen, but failing to spell it out is a guarantee that we will not get a nation of young people capable of meeting the challenges ahead.
Zhao: This I will have to respectfully disagree with. The U.S. has had a decentralized education system forever (until Bush and Obama) and it has become one of the most prosperous, innovative, and democratic nations on earth. The lack of a common prescription of content imposed on all children by the government has not been a vice, but a virtue. As Harvard economists Claudia Goldin and Lawrence Katz wrote in their book The Race between Education and Technology: “We must shed our collective amnesia. America was once the world’s education leader. The rest of the world imported its institutions and its egalitarian ideals spread widely. That alone is a great achievement and one calls for an encore.”
Tucker: Zhao apparently believes that standards mean standardization and standardization would inevitably lead to an inability to produce creative solutions to the problems the workforce will face in the years ahead. That could certainly happen. But it need not happen.
Zhao: Yes, it does not need to, but it does happen, has happened, and is unavoidable. When standards are enforced with high stakes testing, when teachers and principals are evaluated based on students’ test scores, when students’ fate are decided by test scores, the teaching and learning must become standardized and constrained. One does not have to go to China to see this. Just take a look at what happened under NCLB. It did not ask schools to narrow the curriculum, to reduce time for music and the arts, for social studies and science, or for lunch and recess, but it all happened. For the impact of NCLB on instructional time and curriculum, check out these reports (1 and 2)from the Center on Education Policy.
Tucker: It is simply not true that our inability to predict the jobs people will have to do in the future and the demand of creative, entrepreneurial young people relieves us of the obligation to figure out what skills and knowledge all young people need to have before they go their separate ways, or the obligation to translate that list of skills and knowledge into standards and assessments that can drive instruction in our schools.
Zhao: It is simply not true that the Common Core will prepare our children for the future. To conclude, I quote a comment left on my Facebook page by one of my personal heros, former president of America Educational Research Association (AERA) and widely respected educational researcher Gene Glass: “Common Core Standards are idiots’ solution to a misunderstood problem. The problem is an archaic, useless curriculum that will prepare no child for life in 2040 and beyond.”
– – – – – – – – –

Bob Schaffer was the man who blew the whistle on Marc Tucker and Hillary Clinton’s plot to take over American education. Schaffer got their letter recorded in the official Congressional Record years ago. http://www.eagleforum.org/educate/marc_tucker/
Robert Scott was the very wise Education Commissionar who, together with Gov. Rick Perry of Texas, rejected Common Core for Texas –and enraged Sec. of Education Arne Duncan.
Bill Evers, who is a Hoover Institute, Stanford University research fellow, also served on Mitt Romney’s Education Committee. He spoke on the danger of Common Core education this summer, to a standing room only group in Salt Lake City.
Sandra Stotsky served on the official Common Core Validation Committee (and refused to sign off on the standards because, among other things, they cut out classic literature and call it improving education.)
Jim Stergios and Ted Rebarber spoke this summer, here in Salt Lake City, to our senate Education Committee, testifying of the alarming error it was to adopt Common Core on educational and on Constitutional grounds.
This is going to be a great meeting. If you get to go, please leave a comment here, letting others know what you learned.
The 9th problem with the Common Core standards
-by Marion Brady
It’s an incredibly important argument between a smart, veteran eduator, Marion Brady, versus an extremist left-wing educrat, Marc Tucker (whose socialized-U.S -education plot with Hilary Clinton has been known and Congressionally recorded for decades.) https://whatiscommoncore.wordpress.com/2012/06/22/anti-liberty-plot-for-american-education-full-text-of-the-letter-from-marc-tucker-to-hillary-clinton-2/
Marion Brady’s main point, against Tucker and his Common Core:
-
Common Core centralizes control of education
-
micromanages classrooms (by non-educators)
-
blocks all innovation that’s not tied to the core
-
relies on destructive, simplistic tests that fail to take account of the fundamental nature of knowledge and of human complexity.
– And you can read Marc Tucker’s side of the argument here: http://blogs.edweek.org/edweek/top_performers/2012/09/8_problems_with_the_common_core_state_standards_i_dont_think_so.html
My first thought, upon seeing Marc Tucker’s name as author, in print, was, “What!? Marc Tucker can still get published? After his (and Hilary Clinton’s) socialist plot to take over education was made public, published as part of the Congressional records?! Help!” –But read on.
Marc Tucker:
v. Marion Brady:
)
From Brady:
“…Marc Tucker, long-time major player in the current test-based education reform effort, in an Education Week “Top Performers” blog, took me to task with a piece called “8 Problems With the Common Core State Standards? I Don’t Think So.”
My Washington Post piece was a little over 1,000 words. Mr. Tucker’s response was twice that. If I were to respond point by point to his objections to my eight criticisms of the standards— which I’d really like to do — it would almost certainly double that word count. Few readers would stick with me for 4,000 words, even if editors were willing to publish them.
I’ll stand by my criticisms, but try to move the dialogue along by adding a ninth. I’d have included it before, but couldn’t squeeze it into a paragraph.
Mr. Tucker buys the conventional wisdom, that the subjects that make up the core — math, science, language arts, and social studies — “cover” the important stuff that kids need to know, from which it follows that anything that nails down more precisely what actually gets covered is a good thing. Ergo: the Common Core Standards.
He says, “…the core academic disciplines (the core subjects in the school curriculum) provide the conceptual underpinning for deep understanding of virtually everything we want our students to know.”
Most people agree, including most teachers, especially younger ones. That’s what they’ve been taught, and experience hasn’t yet caused them to question orthodoxy.
I disagree, not about the standards providing conceptual underpinning for the core subjects (which I’ve never questioned). I take issue with the contention that the standards provide “deep understanding of virtually everything we want students to know…”
I’m not alone. Buckminster Fuller, Kurt Vonnegut, Alfred North Whitehead, Felix Frankfurter, Harlan Cleveland, Neil Postman… and dozens of other nationally and internationally known and respected people are on my side of the issue.
But we have a problem. The idea we’re trying to get across isn’t part of the current education reform dialogue. That means that in a few hundred words, I have to try to introduce a new (and very abstract) idea, explain why it’s of fundamental importance but at odds with the standards, and offer an alternative.
Here’s that idea, as articulated by Peter M. Senge, a professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. In his book, “The Fifth Discipline,” he says:
From a very early age, we are taught to break apart problems, to fragment the world. This apparently makes complex tasks and subjects more manageable, but we pay a hidden, enormous price. We can no longer see the consequences of our actions; we lose our intrinsic sense of connection to a larger whole.
That “larger whole” is reality. We want kids to make better sense of it. To that end, we send them off to study school subjects that explain various parts of it. We don’t, however, show them how those parts fit together, relate, interact, elaborate, and reinforce each other. When the bell rings, off they go to study a different subject that, as far as they can tell, is little or not at all related to the one they just left.
As this brief slideshow illustrates, this is a first-order problem, and the Common Core Standards ignore it. Locking the core subjects in place tells the world that America thinks a curriculum patched together in 1892 by 10 college administrators, a curriculum that reflects the industrial policy of the era, a curriculum that fails to acknowledge the fundamental, integrated nature of reality, is the best way to organize knowledge.
It’s not. Systems theory as it developed during World War II is far better. Period. It doesn’t replace the core subjects (which I’ve never advocated), just makes them working parts of a single, simpler, more efficient “master” mental organizer.
This is absolutely central to learning. Knowledge grows as we connect bits of it — as we discover relationships between, say, street width and sense of community, between birth order and certain personality traits, between capital investment decisions and political stability.
Compartmentalizing knowledge gets directly in the way of the basic process that makes kids (and the rest of us) smarter.
That systems thinking integrates knowledge isn’t an original idea. I’m just passing it along and offering a way to operationalize it.
A little story: Years ago I realized that what educators like John Goodlad, Neil Postman, Alfred North Whitehead, Ernest Boyer and others were saying in books, articles, and speeches wasn’t making any difference in what was actually happening in classrooms. Knowing it isn’t always easy to translate theory into practice, I wrote a course of study for adolescents that showed how systems theory could help them see the connected nature of all knowledge and the minute-by-minute way they were experiencing it.
I chose to write for middle schoolers because they hadn’t yet been thoroughly programmed by traditional instruction to compartmentalize what they knew, and because an earlier project I’d undertaken for Prentice-Hall, Inc. had led to friendships with several middle school principals around the country.
I contacted them. Would they be willing to pilot my course of study and give me feedback so I could refine it?
Nobody turned me down. Everything was in place for the fall of the year, then No Child Left Behind became law, and that was the end of that. I got letters and phone calls from the principals apologizing for having to back out of their commitment. It was clear to them that raising test scores, not improving kids’ ability to make better sense of experience, was now the name of the education game.
And so it remains. Over the years, with my brother’s help, I’ve continued to play with the course of study, thinking some rebel school system somewhere might pilot and help improve it, but the money and power behind the “standards and accountability” juggernaut probably make it unstoppable. The standards have been swallowed by just about everybody, and as soon as they’ve been digested, Pearson, McGraw-Hill, Educational Testing Service, and other manufacturers of standardized tests will be ready with contracts in hand for computerized tests in numbers sufficient to crash web servers.
The tests, of course, will build in a failure rate set by some faceless decision-maker — an easily operated spigot for meeting stockholder expectations. Open it — boost the failure rate — and up go sales of tests, test prep tools, instructional materials. And, of course, profits.
Even if I’m wrong about the eight other problems with the Common Core Standards (and I’m not), I don’t see any wiggle room on this one. If I’m right, the current reform effort’s centralizing of control of education, its micromanaging of classrooms by non-educators, its blocking of all innovation not tied to the core, and its reliance on destructive, simplistic tests that fail to take account of the fundamental nature of knowledge, and of human complexity and variability, will, in Senge’s words, exact an “enormous price.”
That price will be the inability of our children and our children’s children to cope with a future shaping up to be more challenging than anything humans have thus far faced.”
Thank you, Marion Brady.
This letter, from Marc Tucker to Hillary Clinton (written a decade ago, long before “governors and educators and individual states came up with” the idea of Common Core) –shows the plan of elite politicians to overtake individual state sovereignty of education. This letter is part of the Congressional Record. It really was sent by Marc Tucker to Hillary Clinton. It really does outline a plan to take over American education and turn it into a control system. And it’s really coming true, in the form of Common Core Education.
Marc Tucker
Hillary Clinton
11 November 1992
Hillary Clinton
The Governor’s Mansion
1800 Canter Street
Little Rock, AR 72206
Dear Hillary:
I still cannot believe you won. But utter delight that you did pervades all the circles in which I move. I met last Wednesday in David Rockefeller’s office with him, John Sculley, Dave Barram and David Haselkorn. It was a great celebration. Both John and David R. were more expansive than I have ever seen them — literally radiating happiness. My own view and theirs is that this country has seized its last chance. I am fond of quoting Winston Churchill to the effect that “America always does the right thing — after it has exhausted all the alternatives.” This election, more than anything else in my experience, proves his point.
The subject we were discussing was what you and Bill should do now about education, training and labor market policy. Following that meeting, I chaired another in Washington on the same topic. Those present at the second meeting included Tim Barnicle, Dave Barram, Mike Cohen, David Hornbeck, Hilary Pennington, Andy Plattner, Lauren Resnick, Betsy Brown Ruzzi, Bob Schwartz, Mike Smith and Bill Spring. Shirley Malcom, Ray Marshall and Susan McGuire were also invited. Though these three were not able to be present at last week’s meeting, they have all contributed by telephone to the ideas that follow. Ira Magaziner was also invited to this meeting.
Our purpose in these meetings was to propose concrete actions that the Clinton administration could take — between now and the inauguration, in the first 100 days and beyond. The result, from where I sit, was really exciting. We took a very large leap forward in terms of how to advance the agenda on which you and we have all been working — a practical plan for putting all the major components of the system in place within four years, by the time Bill has to run again.
I take personal responsibility for what follows. Though I believe everyone involved in the planning effort is in broad agreement, they may not all agree on the details. You should also be aware that, although the plan comes from a group closely associated with the National Center on Education and the Economy, there was no practical way to poll our whole Board on this plan in the time available. It represents, then, not a proposal from our Center, but the best thinking of the group I have named.
We think the great opportunity you have is to remold the entire American system for human resources development, almost all of the current components of which were put in place before World War II. The danger is that each of the ideas that Bill advanced in the campaign in the area of education and training could be translated individually in the ordinary course of governing into a legislative proposal and enacted as a program. This is the plan of least resistance. But it will lead to these programs being grafted onto the present system, not to a new system, and the opportunity will have been lost. If this sense of time and place is correct, it is essential that the administration’s efforts be guided by a consistent vision of what it wants to accomplish in the field of human resource development, with respect both to choice of key officials and the program.
What follows comes in three places:
First, a vision of the kind of national — not federal — human resources development system the nation could have. This is interwoven with a new approach to governing that should inform that vision. What is essential is that we create a seamless web of opportunities, to develop one’s skills that literally extends from cradle to grave and is the same system for everyone — young and old, poor and rich, worker and full-time student. It needs to be a system driven by client needs (not agency regulations or the needs of the organization providing the services), guided by clear standards that define the stages of the system for the people who progress through it, and regulated on the basis of outcomes that providers produce for their clients, not inputs into the system.
Second, a proposed legislative agenda you can use to implement this vision. We propose four high priority packages that will enable you to move quickly on the campaign promises:
[Page: E1820]
- The first would use your proposal for an apprenticeship system as the keystone of a strategy for putting a whole new postsecondary training system in place. That system would incorporate your proposal for reforming postsecondary education finance. It contains what we think is a powerful idea for rolling out and scaling up the whole new human resources system nationwide over the next four years, using the (renamed) apprenticeship ideas as the entering wedge.
- The second would combine initiatives on dislocated workers, a rebuilt employment service and a new system of labor market boards to offer the Clinton administration’s employment securityprogram, built on the best practices anywhere in the world. This is the backbone of a system for assuring adult workers in our society that they need never again watch with dismay as their jobs disappear and their chances of ever getting a good job again go with them.
- The third would concentrate on the overwhelming problems of our inner cities, combining elements of the first and second packages into a special program to greatly raise the work-related skills of the people trapped in the core of our great cities.
- The fourth would enable you to take advantage of legislation on which Congress has already been working to advance the elementary and secondary reform agenda.
The other major proposal we offer has to do with government organization for the human resources agenda. While we share your reservations about the hazards involved in bringing reorganization proposals to the Congress, we believe that the one we have come up with minimizes those drawbacks while creating an opportunity for the new administration to move like lightning to implement its human resources development proposals. We hope you can consider the merits of this idea quickly, because, if you decide to go with it or something like it, it will greatly affect the nature of the offers you make to prospective cabinet members.
The Vision
We take the proposals Bill put before the country in the campaign to be utterly consistent with the ideas advanced in America’s Choice, the school restructuring agenda first stated in A Nation Prepared, and later incorporated in the work of the National Alliance for Restructuring Education, and the elaboration of this view that Ray and I tried to capture in our book, Thinking for a Living. Taken together, we think these ideas constitute a consistent vision for a new human resources development system for the United States. I have tried to capture the essence of that vision below.
An Economic Strategy Based on Skill Development
- The economy’s strength is derived from a whole population as skilled as any in the world, working in workplaces organized to take maximum advantage of the skills those people have to offer.
- A seamless system of unending skill development that begins in the home with the very young and continues through school, postsecondary education and the workplace.
The Schools
- Clear national standards of performance in general education (the knowledge and skills that everyone is expected to hold in common) are set to the level of the best achieving nations in the world for students of 16, and public schools are expected to bring all but the most severely handicapped up to that standard. Students get a certificate when they meet this standard, allowing them to go on to the next stage of their education. Though the standards are set to international benchmarks, they are distinctly American, reflecting our needs and values.
- We have a national system of education in which curriculum, pedagogy, examinations, and teacher education and licensure systems are all linked to the national standards, but which provides for substantial variance among states, districts, and schools on these matters. This new system of linked standards, curriculum, and pedagogy will abandon the American tracking system, combining high academic standards with the ability to apply what one knows to real world problems and qualifying all students for a lifetime of learning in the postsecondary system and at work.
- We have a system that rewards students who meet the national standards with further education and good jobs, providing them a strong incentive to work hard in school.
- Our public school systems are reorganized to free up school professionals to make the key decisions about how to use all the available resources to bring students up to the standards. Most of the federal, state, district and union rules and regulations that now restrict school professionals’ ability to make these decisions are swept away, though strong measures are in place to make sure that vulnerable populations get the help they need. School professionals are paid at a level comparable to that of other professionals, but they are expected to put in a full year, to spend whatever time it takes to do the job and to be fully accountable for the results of their work. The federal, state and local governments provide the time, staff development resources, technology and other support needed for them to do the job. Nothing less than a wholly restructured school system can possibly bring all of our students up to the standards only a few have been expected to meet up to now.
- There is a real — aggressive — program of public choice in our schools, rather than the flaccid version that is widespread now.
- All students are guaranteed that they will have a fair shot at reaching the standards: that is, that whether they make it or not depends on the effort they are willing to make, and nothing else. School delivery standards are in place to make sure this happens. These standards have the same status in the system as the new student performance standards, assuring that the quality of instruction is high everywhere, but they are fashioned so as not to constitute a new bureaucratic nightmare.
Postsecondary Education and Work Skills
- All students who meet the new national standards for general education are entitled to the equivalent of three more years of free additional education. We would have the federal and state governments match funds to guarantee one free year of college education to everyone who meets the new national standards for general education. So a student who meets the standard at 16 would be entitled to two free years of high school and one of college. Loans, which can be forgiven for public service, are available for additional education beyond that. National standards for sub-baccalaureate college-level professional and technical degrees and certificates will be established with the participation of employers, labor and higher education. These programs will include both academic study and structured on-the-job training. Eighty percent or more of American high school graduates will be expected to get some form of college degree, though most of them less than a baccalaureate. These new professional and technical certificates and degrees typically are won within three years of acquiring the general education certificate, so, for most postsecondary students, college will be free. These professional and technical degree programs will be designed to link to programs leading to the baccalaureate degree and higher degrees. There will be no dead ends in this system. Everyone who meets the general education standard will be able to go to some form of college, being able to borrow all the money they need to do so, beyond the first free year.
(This idea of post-secondary professional and technical certificates captures all of the essentials of the apprenticeship idea, while offering none of its drawbacks (see below). But it also makes it clear that those engaged in apprentice-style programs are getting more than narrow training; they are continuing their education for other purposes as well, and building a base for more education later. Clearly, this idea redefines college. Proprietary schools, employers and community-based organizations will want to offer these programs, as well as community colleges and four-year institutions, but these new entrants will have to be accredited if they are to qualify to offer the programs.)
- Employers are not required to provide slots for the structured on-the-job training component of the program but many do so, because they get first access to the most accomplished graduates of these programs, and they can use these programs to introduce the trainees to their own values and way of doing things.
- The system of skill standards for technical and professional degrees is the same for students just coming out of high school and for adults in the workforce. It is progressive, in the sense that certificates and degrees for entry level jobs lead to further professional and technical education programs at higher levels. Just as in the case of the system for the schools, though the standards are the same everywhere (leading to maximum mobility for students),the curricula can vary widely and programs can be custom designed to fit the needs of full-time and part-time students with very different requirements. Government grant and loan programs are available on the same terms to full-time and part-time students, as long as the programs in which they are enrolled are designed to lead to certificates and degrees defined by the system of professional and technical standards.
- The national system of professional and technical standards is designed much like the multistate bar, which provides a national core around which the states can specify additional standards that meet their unique needs. There are national standards and exams for no more than 20 broad occupational areas, each of which can lead to many occupations in a number of related industries. Students who qualify in any one of these areas have the broad skills required by a whole family of occupations, and most are sufficiently skilled to enter the workforce immediately, with further occupation-specific skills provided by their union or employer. Industry and occupational groups can voluntarily create standards building on these broad standards for their own needs, as can the states. Students entering the system are first introduced to very broad occupational groups, narrowing over time to concentrate on acquiring the skills needed for a cluster of occupations. This modular system provides for the initiative of particular states and industries while at the same time providing for mobility across states and occupations by reducing the time and cost entailed in moving from one occupation to another. In this way, a balance is established between the kinds of generic skills needed to function effectively in high performance work organizations and the skills needed to continue learning quickly and well through a lifetime of work, on the one hand, and the specific skills needed to perform at a high level in a particular occupation on the other.
- Institutions receiving grant and loan funds under this system are required to provide information to the public and to government agencies in a uniform format. This information covers enrollment by program, costs and success rates for students of different backgrounds and characteristics, and career outcomes for those students, thereby enabling students to make informed choices among institutions based on cost and performance. Loan defaults are reduced to a level close to zero, both because programs that do not deliver what they promise are not selected by prospective students and because the new postsecondary loan system uses the IRS to collect what is owed from salaries and wages as they are earned.
[Page: E1821]
Education and Training for Employed and Unemployed Adults
- The national system of skills standards establishes the basis for the development of a coherent, unified training system. That system can be accessed by students coming out of high school, employed adults who want to improve their prospects, unemployed adults who are dislocated and others who lack the basic skills required to get out of poverty. But it is all the same system. There are no longer any parts of it that are exclusively for the disadvantaged,though special measures are taken to make sure that the disadvantaged are served. It is a system for everyone, just as all the parts of the system already described are for everyone. So the people who take advantage of this system are not marked by it as damaged goods. The skills they acquire are world class, clear and defined in part by the employers who will make decisions about hiring and advancement.
- The new general education standard becomes the target for all basic education programs, both for school dropouts and adults. Achieving that standard is the prerequisite for enrollment in all professional and technical degree programs. A wide range of agencies and institutions offer programs leading to the general education certificate, including high schools, dropout recovery centers, adult education centers, community colleges, prisons and employers. These programs are tailored to the needs of the people who enroll in them. All the programs receiving government grant or loan funds that come with dropouts and adults for enrollment in programs preparing students to meet the general education standard must release the same kind of data required of the postsecondary institutions on enrollment, program description, cost and success rates. Reports are produced for each institution and for the system as a whole showing differential success rates for each major demographic group.
- The system is funded in four different ways, all providing access to the same or a similar set of services. School dropouts below the age of 21 are entitled to the same amount of funding from the same sources that they would have been entitled to had they stayed in school. Dislocated workers are funded by the federal government through the federal programs for that purpose and by state unemployment insurance funds. The chronically unemployed are funded by federal and state funds established for that purpose. Employed people can access the system through the requirement that their employers spend an amount equal to 1-1/2 percent of their salary and wage bill on training leading to national skill certification. People in prison could get reductions in their sentences by meeting the general education standard in a program provided by the prison system. Any of these groups can also use the funds in their individual training account, if they have any, the balances in their grant entitlement or their access to the student loan fund.
Labor Market Systems
- The Employment Service is greatly upgraded and separated from the Unemployment Insurance Fund. All available front-line jobs — whether public or private — must be listed in it by law. (This provision must be carefully designed to make sure that employers will not be subject to employment suits based on the data produced by this system — if they are subject to such suits, they will not participate.) All trainees in the system looking for work are entitled to be listed in it without a fee. So it is no longer a system just for the poor and unskilled, but for everyone. The system is fully computerized. It lists not only job openings and job seekers (with their qualifications) but also all the institutions in the labor market area offering programs leading to the general education certificate and those offering programs leading to the professional and technical college degrees and certificates, along with all the relevant data about the costs, characteristics and performance of those programs — for everyone and for special populations. Counselors are available to any citizen to help them assess their needs, plan a program and finance it, and, once they are trained, to find an opening.
- A system of labor market boards is established at the local, state and federal levels to coordinate the systems for job training, postsecondary professional and technical education, adult basic education, job matching and counseling. The rebuilt Employment Service is supervised by these boards. The system’s clients no longer have to go from agency to agency filling out separate applications for separate programs. It is all taken care of at the local labor market board office by one counselor accessing the integrated computer-based program, which makes it possible for the counselor to determine eligibility for all relevant programs at once, plan a program with the client and assemble the necessary funding from all the available sources. The same system will enable counselor and client to array all the relevant program providers side by side, assess their relative costs and performance records and determine which providers are best able to meet the client’s needs based on performance.
Some Common Features
- Throughout, the object is to have a performance- and client-oriented system, to encourage local creativity and responsibility by getting local people to commit to high goals and organize to achieve them, sweeping away as much of the rules, regulations and bureaucracy that are in their way as possible, provided that they are making real progress against their goals. For this to work, the standards at every level of the system have to be clear; every client has to know what they have to accomplish in order to get what they want out of the system. The service providers have to be supported in the task of getting their clients to the finish line and rewarded when they are making real progress toward that goal. We would sweep away means-tested programs, because they stigmatize their recipients and alienate the public, replacing them with programs that are for everyone, but also work for the disadvantaged. We would replace rules defining inputs with rules defining outcomes and the rewards for achieving them. This means, among other things, permitting local people to combine as many federal programs as they see fit, provided that the intended beneficiaries are progressing toward the right outcomes (there are now 23 separate federal programs for dislocated workers!). We would make individuals, their families and whole communities the unit of service, not agencies, programs and projects. Wherever possible, we would have service providers compete with one another for funds that come with the client, in an environment in which the client has good information about the cost and performance record of the competing providers. Dealing with public agencies — whether they are schools or the employment service — should be more like dealing with Federal Express than with the old Post Office.
This vision, as I pointed out above, is consistent with everything Bill proposed as a candidate. But it goes beyond those proposals, extending them from ideas for new programs to a comprehensive vision of how they can be used as building blocks for a whole new system. But this vision is very complex, will take a long time to sell, and will have to be revised many times along the way. The right way to think about it is as an internal working document that forms the background for a plan, not the plan itself. One would want to make sure that the specific actions of the new administration were designed, in a general way, to advance this agenda as it evolved, while not committing anyone to the details, which would change over time.
Everything that follows is cast in the frame of strategies for bringing the new system into being, not as a pilot program, not as a few demonstrations to be swept aside in another administration, but everywhere, as the new way of doing business.
In the sections that follow, we break these goals down into their main components and propose an action plan for each.
[Page: E1822]
Major Components of the Program
The preceding section presented a vision of the system we have in mind chronologically from the point of view of an individual served by it. Here we reverse the order, starting with descriptions of program components designed to serve adults, and working our way down to the very young.
HIGH SKILLS FOR ECONOMIC COMPETITIVENESS PROGRAM
Developing System Standards
- Create National Board for Professional and Technical Standards. Board is private not-for-profit chartered by Congress. Charter specifies broad membership composed of leading figures from higher education, business, labor, government and advocacy groups. Board can receive appropriated funds from Congress, private foundations, individuals, and corporations. Neither Congress nor the executive branch can dictate the standards set by the Board. But the Board is required to report annually to the President and the Congress in order to provide for public accountability. It is also directed to work collaboratively with the states and cities involved in the Collaborative Design and Development Program (see below) in the development of the standards.
- Charter specifies that the National Board will set broad performance standards (not time-in-the-seat standards or course standards) for college-level Professional and Technical certificates and degrees in not more than 20 areas and develops performance examinations for each. The Board is required to set broad standards of the kind described in the vision statement above and is not permitted to simply reify the narrow standards that characterize many occupations now. (More than 2,000 standards currently exist, many for licensed occupations — these are not the kinds of standards we have in mind.) It also specifies that the programs leading to these certificates and degrees will combine time in the classroom with time at the work-site in structured on-the-job training. The standards assume the existence of (high school level) general education standards set by others. The new standards and exams are meant to be supplemented by the states and by individual industries and occupations. Board is responsible for administering the exam system and continually updating the standards and exams.
Legislation creating the Board is sent to the Congress in the first six months of the administration, imposing a deadline for creating the standards and the exams within three years of passage of the legislation.
Commentary:
The proposal reframes the Clinton apprenticeship proposal as a college program and establishes a mechanism for setting the standards for the program. The unions are adamantly opposed to broad based apprenticeship programs by that name. Focus groups conducted by JFF and others show that parents everywhere want their kids to go to college, not to be shunted aside into a non-college apprenticeship “vocational” program. By requiring these programs to be a combination of classroom instruction and structured OJT, and creating a standard-setting board that includes employers and labor, all the objectives of the apprenticeship idea are achieved, while at the same time assuring much broader support for the idea, as well as a guarantee that the program will not become too narrowly focussed on particular occupations. It also ties the Clinton apprenticeship idea to the Clinton college funding proposal in a seamless web. Charging the Board with creating not more than 20 certificate or degree categories establishes a balance between the need to create one national system on the one hand with the need to avoid creating a cumbersome and rigid national bureaucracy on the other. This approach provides lots of latitude for individual industry groups, professional groups and state authorities to establish their own standards, while at the same time avoiding the chaos that would surely occur if they were the only source of standards. The bill establishing the Board should also authorize the executive branch to make grants to industry groups, professional societies, occupational groups and states to develop standards and exams. Our assumption is that the system we are proposing will be managed so as to encourage the states to combine the last two years of high school and the first two years of community college into three year programs leading to college degrees and certificates. Proprietary institutions, employers and community-based organizations could also offer these programs, but they would have to be accredited to offer these college-level programs. Eventually, students getting their general education certificates might go directly to community college or to another form of college, but the new system should not require that.
Collaborative Design and Development Program
The object is to create a single comprehensive system for professional and technical education that meets the requirements of everyone from high school students to skilled dislocated workers, from the hard core unemployed to employed adults who want to improve their prospects. Creating such a system means sweeping aside countless programs, building new ones, combining funding authorities, changing deeply embedded institutional structures, and so on. The question is how to get from where we are to where we want to be. Trying to ram it down everyone’s throat would engender overwhelming opposition. Our idea is to draft legislation that would offer an opportunity for those states — and selected large cities — that are excited about this set of ideas to come forward and join with each other and with the federal government in an alliance to do the necessary design work and actually deliver the needed services on a fast track. The legislation would require the executive branch to establish a competitive grant program for these states and cities and to engage a group of organizations to offer technical assistance to the expanding set of states and cities engaged in designing and implementing the new system. This is not the usual large scale experiment, nor is it a demonstration program. A highly regarded precedent exists for this approach in the National Science Foundation’s SSI program. As soon as the first set of states is engaged, another set would be invited to participate, until most or all the states are involved. It is a collaborative design, rollout and scale-up program. It is intended to parallel the work of the National Board for College Professional and Technical Standards, so that the states and cities (and all their partners) would be able to implement the new standards as soon as they become available, although they would be delivering services on a large scale before that happened. Thus, major parts of the whole system would be in operation in a majority of the states within three years from the passage of the initial legislation. Inclusion of selected large cities in this design is not an afterthought. We believe that what we are proposing here for the cities is the necessary complement to a large scale job-creation program for the cities. Skill development will not work if there are no jobs, but job development will not work without a determined effort to improve the skills of city residents. This is the skill development component.
- Participants
- volunteer states, counterpart initiative for cities.
- 15 states, 15 cities selected to begin in first year. 15 more in each successive year.
- 5 year grants (on the order of $20 million per year to each state, lower amounts to the cities) given to each, with specific goals to be achieved by the third year, including program elements in place (e.g., upgraded employment service), number of people enrolled in new professional and technical programs and so on.
- a core set of High Performance Work Organization firms willing to participate in standard setting and to offer training slots and mentors.
- Criteria for Selection
- strategies for enriching existing co-op, tech prep and other programs to meet the criteria.
- commitment to implementing new general education standard in legislation.
- commitment to implementing the new Technical and Professional skills standards for college.
- commitment to developing an outcome- and performance-based system for human resources development system.
- commitment to new role for employment service.
- commitment to join with others in national design and implementation activity.
- Clients
- young adults entering workforce.
- dislocated workers.
- long-term unemployed.
- employed who want to upgrade skills.
- Program Components
- institute own version of state and local labor market boards. Local labor market boards to involve leading employers, labor representatives, educators and advocacy group leaders in running the redesigned employment service, running intake system for all clients, counseling all clients, maintaining the information system that will make the vendor market efficient and organizing employers to provide job experience and training slots for school youth and adult trainees.
- rebuild employment service as a primary function of labor market boards.
- develop programs to bring dropouts and illiterates up to general education certificate standard. Organize local alternative providers, firms to provide alternative education, counseling, job experience and placement services to these clients.
- develop programs for dislocated workers and hard-core unemployed (see below).
- develop city- and state-wide programs to combine the last two years of high school and the first two years of colleges into three-year programs after acquisition of the general education certificate to culminate in college certificates and degrees. These programs should combine academics and structured on-the-job training.
- develop uniform reporting system for providers, requiring them to provide information in that format on characteristics of clients, their success rates by program, and the costs of those programs. Develop computer-based system for combining this data at local labor market board offices with employment data from the stateso that counselors and clients can look at programs offered by colleges and other vendors in terms of cost, client characteristics, program design, and outcomes. Including subsequent employment histories for graduates.
- design all programs around the forthcoming general education standards and the standards to be developed by the National Board for College Professional and Technical Standards.
- create statewide program of technical assistance to firms on high performance work organization and help them develop quality programs for participants in Technical and Professional certificate and degree programs. (It is essential that these programs be high quality, nonbureaucratic and voluntary for the firms.)
- participate with other states and the national technical assistance program in the national alliance effort to exchange information and assistance among all participants.
[Page: E1823]
- National technical assistance to participants
- executive branch authorized to compete opportunity to provide the following services (probably using a Request For Qualifications):
- state-of-the art assistance to the states and cities related to the principal program components (e.g., work reorganization, training, basic literacy, funding systems, apprenticeship systems, large scale data management systems, training systems for the HR professionals who make the whole system work, etc.). A number of organizations would be funded. Each would be expected to provide information and direct assistance to the states and cities involved, and to coordinate their efforts with one another.
- it is essential that the technical assistance function include a major professional development component to make sure the key people in the states and cities upon whom success depends have the resources available to develop the high skills required. Some of the funds for this function should be provided directly to the states and cities, some to the technical assistance agency.
- coordination of the design and implementation activities of the whole consortium, document results, prepare reports, etc. One organization would be funded to perform this function.
Dislocated Workers Program
- new legislation would permit combining all dislocated workers programs at redesigned employment service office. Clients would, in effect, receive vouchers for education and training in amounts determined by the benefits for which they qualify. Employment service case managers would qualify client worker for benefits and assist the client in the selection of education and training programs offered by provider institutions. Any provider institutions that receive funds derived from dislocated worker programs are required to provide information on costs and performance of programs in uniform format described above. This consolidated and voucherized dislocated workers program would operate nationwide. It would be integrated with Collaborative Design and Development Program in those states and cities in which that program functioned. It would be built around the general education certificate and the Professional and Technical Certificate and Degree Program as soon as those standards were in place. In this way, programs for dislocated workers would be progressively and fully integrated with the rest of the national education and training system.
Levy-Grant System
- this is the part of the system that provides funds for currently employed people to improve their skills. Ideally, it should specifically provide means whereby front-line workers can earn their general education credential (if they do not already have one) and acquire Professional and Technical Certificates and degrees in fields of their choosing.
- everything we have heard indicates virtually universal opposition in the employer community to the proposal for a 1-1/2% levy on employers for training to support the costs associated with employed workers gaining these skills, whatever the levy is called. We propose that Bill take a leaf out of the German book. One of the most important reasons that large German employers offer apprenticeship slots to German youngsters is that they fear, with good reason, that if they don’t volunteer to do so, the law will require it. Bill could gather a group of leading executives and business organization leaders, and tell them straight out that he will hold back on submitting legislation to require a training levy, provided that they commit themselves to a drive to get employers to get their average expenditures on front-line employee training up to 2% of front-line employee salaries and wages within two years. If they have not done so within that time, then he will expect their support when he submits legislation requiring the training levy. He could do the same thing with respect to slots for structured on-the-job training.
College Loan/Public Service Program
- we presume that this program is being designed by others and so have not attended to it. From everything we know about it, however, it is entirely compatible with the rest of what is proposed here. What is, of course, especially relevant here, is that our reconceptualization of the apprenticeship proposal as a college-level education program, combined with our proposal that everyone who gets the general education credential be entitled to a free year of higher education (combined federal and state funds) will have a decided impact on the calculations of cost for the college loan/public service program.
Assistance for Dropouts are the Long-Term Unemployed
- the problem of upgrading the skills of high school dropouts and the adult hard core unemployed is especially difficult. It is also at the heart of the problem of our inner cities. All the evidence indicates that what is needed is something with all the important characteristics of a non-residential Job Corps-like program. The problem with the Job Corps is that it is operated directly by the federal government and is therefore not embedded at all in the infrastructure of local communities. The way to solve this problem is to create a new urban program that is locally — not federally — organized and administered, but which must operate in a way that uses something like the federal standards for contracting for Job Corps services. In this way, local employers, neighborhood organizations and other local service providers could meet the need, but requiring local authorities to use the federal standards would assure high quality results. Programs for high school dropouts and the hard-core unemployed would probably have to be separately organized, though the services provided would be much the same. Federal funds would be offered on a matching basis with state and local funds for this purpose. These programs should be fully integrated with the revitalized employment service. The local labor market board would be the local authority responsible for receiving the funds and contracting with providers for the services. It would provide diagnostic, placement and testing services. We would eliminate the targeted jobs credit and use the money now spent on that program to finance these operations. Funds can also be used from the JOBS program in the welfare reform act. This will not be sufficient, however, because there is currently no federal money available to meet the needs of hard-core unemployed males (mostly Black) and so new monies will have to be appropriated for the purpose.
Commentary:
As you know very well, the High Skills, Competitive Workforce Act sponsored by Senators Kennedy and Hatfield and Congressmen Gephardt and Regula provides a ready-made vehicle for advancing many of the ideas we have outlined. To foster a good working relationship with the Congress, we suggest that, to the extent possible, the framework of these companion bills be used to frame the President’s proposals. You may not know that we have put together a large group of representatives of Washington-based organizations to come to a consensus around the ideas in America’s Choice. They are full of energy and very committed to this joint effort. If they are made part of the process of framing the legislative proposals, they can be expected to be strong support for them when they arrive on the Hill. As you think about the assembly of these ideas into specific legislative proposals, you may also want to take into account the packaging ideas that come later in this letter.
ELEMENTARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION PROGRAM
The situation with respect to elementary and secondary education is very different from adult education and training. In the latter case, a new vision and a whole new structure is required. In the former, there is increasing acceptance of a new vision and structure among the public at large, within the relevant professional groups and in Congress. There is also a lot of existing activity on which to build. So we confine ourselves here to describing some of those activities that can be used to launch the Clinton education program.
Standard Setting
Legislation to accelerate the process of national standard setting in education was contained in the conference report on S.2 and HR 4323 that was defeated on a recent cloture vote. Solid majorities were behind the legislation in both houses of Congress. While some of us would quarrel with a few of the details, we think the new administration should support the early reintroduction of this legislation with whatever changes it thinks fit. This legislation does not establish a national body to create a national examination system. We think that is the right choice for now.
[Page: E1824]
Systemic Chance in Public Education
The conference report on S.2 and HR 4323 also contained a comprehensive program to support systemic change in public education. Here again, some of us would quibble with some of the particulars, but we believe that the administration’s objectives would be well served by endorsing the resubmission of this legislation, modified as it sees fit.
Federal Programs for the Disadvantaged
The established federal education programs for the disadvantaged need to be thoroughly overhauled to reflect an emphasis on results for the students rather than compliance with the regulations. A national commission on Chapter 1, the largest of these programs, chaired by David Hornbeck, has designed a radically new version of this legislation, with the active participation of many of the advocacy groups. Other groups have been similarly engaged. We think the new administration should quickly endorse the work of the national commission and introduce its proposals early next year. It is unlikely that this legislation will pass before the deadline — two years away — for the reauthorization of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act, but early endorsement of this new approach by the administration will send a strong signal to the Congress and will greatly affect the climate in which other parts of the act will be considered.
Public Choice Technology, Integrated Health and Human Services, Curriculum Resources, High Performance Management, Professional Development and Research and Development
The restructuring of the schools that is envisioned in S.2 and HR 4323 is not likely to succeed unless the schools have a lot of information about how to do it and real assistance in getting it done. The areas in which this help is needed are suggested by the heading of this section. One of the most cost-effective things the federal government could do is to provide support for research, development and technical assistance of the schools on these topics. The new Secretary of Education should be directed to propose a strategy for doing just that, on a scale sufficient to the need. Existing programs of research, development and assistance should be examined as possible sources of funds for these purposes. Professional development is a special case. To build the restructured system will require an enormous amount of professional development and the time in which professionals can take advantage of such a resource. Both cost a lot of money. One of the priorities for the new education secretary should be the development of strategies for dealing with these problems. But here, as elsewhere, there are some existing programs in the Department of Education whose funds can be redirected for this purpose, programs that are not currently informed by the goals that we have spelled out. Much of what we have in mind here can be accomplished through the reauthorization of the Office of Educational Research and Improvement. Legislation for that reauthorization was prepared for the last session of Congress, but did not pass. That legislation was informed by a deep distrust of the Republican administration, rather than the vision put forward by the Clinton campaign, but that can and should be remedied on the next round.
Early Childhood Education
The president-elect has committed himself to a great expansion in the funding of Head Start. We agree. But the design of the program should be changed to reflect several important requirements. The quality of professional preparation for the people who staff these programs is very low and there are no standards that apply to their employment. The same kind of standard setting we have called for in the rest of this plan should inform the approach to this program. Early childhood education should be combined with quality day care to provide wrap-around programs that enable working parents to drop off their children at the beginning of the workday and pick them up at the end. Full funding for the very poor should be combined with matching funds to extend the tuition paid by middle class parents to make sure that these programs are not officially segregated by income. The growth of the program should be phased in, rather than done all at once, so that quality problems can be addressed along the way, based on developing examples of best practice. These and other related issues need to be addressed, in our judgment, before the new administration commits itself on the specific form of increased support for Head Start.
Putting the package together:
Here we remind you of what we said at the beginning of this letter about timing the legislative agenda. We propose that you assemble the ideas just described into four high priority packages that will enable you to move quickly on the campaign promises:
- The first would use your proposal for an apprenticeship system as the keystone of the strategy for putting the whole new postsecondary training system in place. It would consist of the proposal for postsecondary standards, the Collaborative Design and Development proposal, the technical assistance proposal and the postsecondary education finance proposal.
- The second would combine the initiatives on dislocated workers, the rebuilt employment service and the new system of labor market boards as the Clinton administration’s employment security program, built on the best practices anywhere in the world. This is the backbone of a system for assuring adult workers in our society that they need never again watch with dismay as their jobs disappear and their chances of ever getting a good job again go with them.
- The third would concentrate on the overwhelming problems of our inner cities, combining most of the elements of the first and second packages into a special program to greatly raise the work-related skills of the people trapped in the core of our great cities.
- The fourth would enable you to take advantage of legislation on which Congress has already been working to advance the elementary and secondary reform agenda. It would combine the successor to HR 4323 and S.2 (incorporating the systemic reforms agenda and the board for student performance standards), with the proposal for revamping Chapter 1.
Organizing the Executive Branch for Human Resouces Development
The issue here is how to organize the federal government to make sure that the new system is actually built as a seamless web in the field, where it counts, and that program gets a fast start with a first-rate team behind it.
We propose, first, that the President appoint a National Council on Human Resources Development. It would consist of the relevant key White House officials, cabinet members and members of Congress. It would also include a small number of governors, educators, business executives, labor leaders and advocates for minorities and the poor. It would be established in such a way as to assure continuity of membership across administrations, so that the consensus it forges will outlast any one administration. It would be charged with recommending broad policy on a national system of human resources development to the President and the Congress, assessing the effectiveness and promise of current programs and proposing new ones. It would be staffed by senior officials on the Domestic Policy Council staff of the President.
Second, we propose that a new agency be created, the National Institute for Learning, Work and Service. Creation of this agency would signal instantly the new administration’s commitment to putting the continuing education and training of the `forgotten half’ on a par with the preparation of those who have historically been given the resources to go to ‘college,’ and to integrate the two systems, not with a view to dragging down the present system and those it serves, but rather to make good on the promise that everyone will have access to the kind of education that only a small minority have had access to up to now. To this agency would be assigned the functions now performed by the assistant secretary for employment and training, the assistant secretary for vocational education and the assistant secretary for higher education. The agency would be staffed by people specifically recruited from all over the country for the purpose. The staff would be small, high powered and able to move quickly to implement the policy initiatives of the new President in the field of human resources development.
The closest existing model to what we have in mind is the National Science Board and the National Science Foundation, with the Council in the place of the Board and the Institute in the place of the Foundation. But our council would be advisory, whereas the Board is governing. If you do not like the idea of a permanent Council, you might consider the idea of a temporary President’s Task Force, constituted much as the Council would be.
In this scheme, the Department of Education would be free to focus on putting the new student performance standards in place and managing the programs that will take the leadership in the national restructuring of the schools. Much of the financing and disbursement functions of the higher education program would move to the Treasury Department, leaving the higher education staff in the new Institute to focus on matters of substance.
In any case, as you can see, we believe that some extraordinary measure well short of actually merging the departments of labor and education is required to move the new agenda with dispatch.
Getting Consensus on the Vision
Radical changes in attitudes, values and beliefs are required to move any combination of these agendas. The federal government will have little direct leverage on many of the actors involved. For much of what must be done, a new, broad consensus will be required. What role can the new administration play in forging that consensus and how should it go about doing it?
At the narrowest level, the agenda cannot be moved unless there is agreement among the governors, the President and the Congress. Bill’s role at the Charlottesville summit leads naturally to a reconvening of that group, perhaps with the addition of key members of Congress and others.
But we think that having an early summit on the subject of the whole human resources agenda would be risky, for many reasons. Better to build on Bill’s enormous success during the campaign with national talk shows, in school gymnasiums and the bus trips. He could start on the consensus-building progress this way, taking his message directly to the public, while submitting his legislative agenda and working it on the Hill. After six months or so, when the public has warmed to the ideas and the legislative packages are about to get into hearings, then you might consider some form of summit, broadened to include not only the governors, but also key members of Congress and others whose support and influence are important. This way, Bill can be sure that the agenda is his, and he can go into it with a groundswell of support behind him.
• • •
That’s it. None of us doubt that you have thought long and hard about many of these things and have probably gone way beyond what we have laid out in many areas. But we hope that there is something here that you can use. We would, of course, be very happy to flesh out these ideas at greater length and work with anyone you choose to make them fit the work that you have been doing.
Very best wishes from all of us to you and Bill.
[signed: Marc]
Marc Tucker
END
|




















